Last updated November 11, 2022
The importance of opportunity cost for SMEs
In this blog post, we will discuss the concept of opportunity costs and the importance of opportunity costs for SME entrepreneurs. Especially when it comes to marketing expenses, they are quite often overlooked. We explain what opportunity costs are and how to use this knowledge to make better decisions.
What are opportunity costs?
Opportunity cost is a concept from microeconomics. The definition reads:
Opportunity cost = (Proceeds from unchosen option - Proceeds from chosen option).
That return does not have to be just money; it can also be time or effort that the choice requires. Entrepreneurs make choices all the time. Time or budget spent on A, is not spendable on B. But what would a different choice have yielded? In other words, what is the relative cost of the choice made?
Suppose a lawyer chooses to cut his own grass. At that time, he could also have been working and making money. Enough to hire a landscaper. By mowing himself, he incurs a cost, so to speak: the lost revenue from a claim.
Explicit and implicit costs
When determining opportunity costs, examine explicit costs as well as implicit costs. Explicit costs are those directly associated with a choice. These are out-of-pocket costs, that is, costs that are actually incurred. Consider, for example, wages, rent, overhead, materials, repairs.
Implicit costs, less visible
Implicit costs are not visible. For example, using a company bus for a move. The bus can then not be used to deliver orders. No invoice has to be paid but there are costs. Or: someone who is normally charged €150 per hour to customers but is away for 2 hours not billable to pick up an order. That's €300 implied cost versus having the order delivered by the supplier.
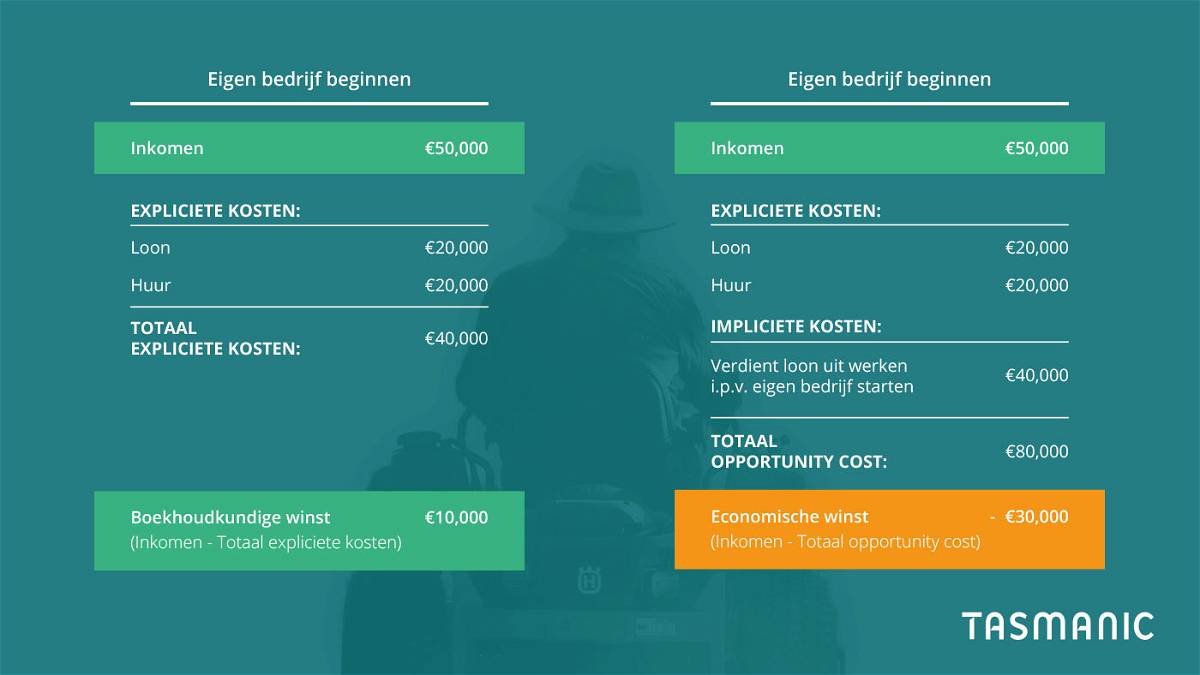
Opportunity costs in business operations
How do you use the concept of opportunity cost to make better decisions in your operations? Determine the potential benefits and costs of all choices, both explicit and implicit. Explicit costs are usually included but implicit costs are not. An example we often see in practice: a web development agency is chosen based on price (explicit costs). Then it is decided to stimulate the growth of the company with online marketing. Then it turns out that the website is not suitable for this purpose and investments must be made in the website first, causing growth to start later.
Cost and opportunity costs in online marketing
Online marketing is a business-critical process for many SMEs. It makes sense then to want to perform it in-house. But it requires specialist knowledge and assessing whether someone is really suitable is often difficult. And that is in the event that candidates present themselves at all. Is it interesting enough for scarce talent to work for 1 company?
So the first choice is: make or buy, execute in-house or buy externally.
In the case of in-house execution, the opportunity costs include:
- The time current employees have to spend on the process of hiring someone.
- Office space costs.
- The money that is not available to make other investments because it is spent on salary and other benefits.
- Lost sales as long as no action is taken because a suitable candidate has not yet been found.
If the choice is buy: outsource externally, there are other opportunity costs that come with it:
- Revenue growth: not all parties will grow you equally. A small difference in percentage can be a big difference in revenue in a year.
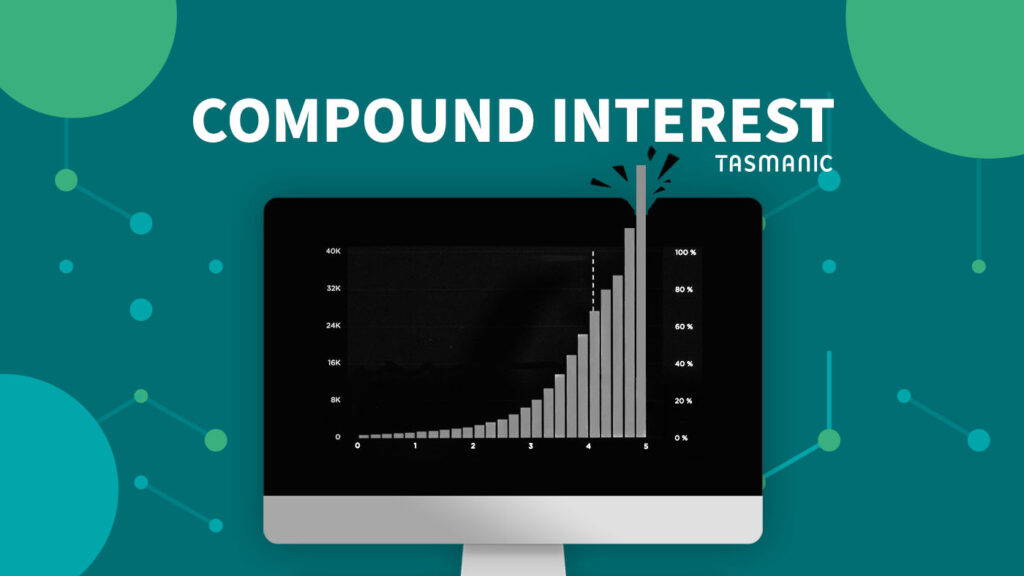
- Growth in enterprise value: not only does turnover grow, but with it enterprise value for shareholders. By missing out on sales growth and thus business value, you create a negative rente-op-rente effect.
- Competitive position: a worsened competitive position can cause major costs in the future. Companies with a strong position spend relatively less money to maintain their position.
- Employing your own staff: outsourcing never means you don't have to do anything yourself at all. Include these costs as well.
Key learning points
- Not all the costs of a choice are visible. Consider also the implicit costs of choices.
- Money and time can only be spent 1 time. Spend them where they have the most impact on business goals.
- Online marketing is a business-critical process for many SMEs and has a major impact on revenue development and business value development.
- The potential opportunity costs of choosing an online marketing partner are thus large and often underestimated.
Is your company missing opportunities?
Request our no-obligation performance scan














 Team
Team FAQ
FAQ Vacancies
Vacancies Contac
Contac AWR
AWR Ahrefs
Ahrefs Channable
Channable ContentKing
ContentKing Leadinfo
Leadinfo Optmyzr
Optmyzr Qooqie
Qooqie Hubspo
Hubspo Semrush
Semrush